Busting Common SSL Certificate Myths
In the digital era, websites are crucial for work and play. But with all the data flying around, we need to keep them secure. That’s where SSL certificates come in. SSL certificates, or Secure Sockets Layer certificates, are digital certificates that facilitate a secure, encrypted connection between a website and its users.
But hold up! There are many myths about SSL certificates that need to be busted. Let’s debunk them and get a better grip on website security!
Myth #1: SSL Certificates are Only Necessary for E-Commerce Websites
Clearing the Facts: SSL certificates are essential for website security, regardless of the type of website. One of the most common misconceptions about SSL certificates is that they are only necessary for e-commerce websites. This myth stems from the belief that SSL certificates are only needed to secure credit card information during online transactions. However, this is far from the truth.
Any website that collects personal information from its users, including names, email addresses, or passwords, needs SSL certificates to protect that data. This includes websites such as blogs, news sites, and forums, where users might submit personal information to comment or participate in discussions. Without SSL certificates, this information can be intercepted and stolen by hackers who might use it for malicious purposes. Don’t fall for the myth that SSL certificates are only for online shops – they’re for everyone!
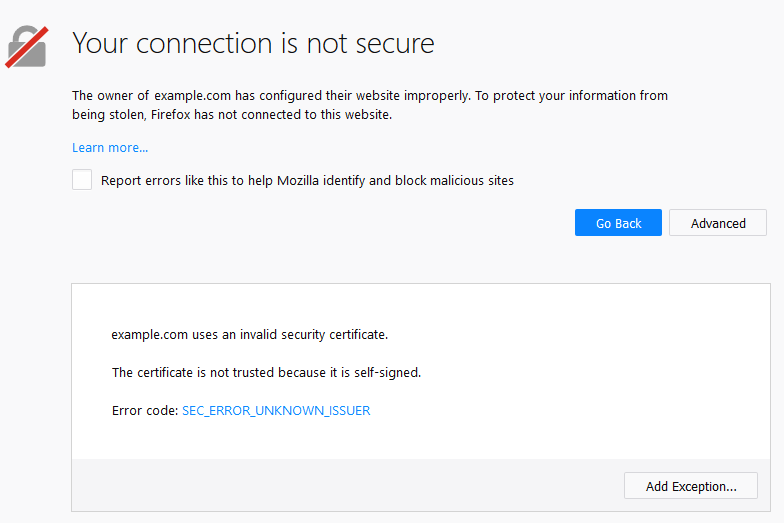
Myth #2: Self-Signed Certificates are Enough to Secure Your Website
Sure, self-signed certificates might seem like a cost-effective solution for testing and piloting your website. They’re easy to create, and you don’t need to pay registration fees. But here’s the fact: they won’t cut it when it comes to gaining the trust of your customers, browsers, search engines, and other third parties.
One of the main reasons for this is that self-signed certificates lack the validation and trust that comes with SSL certificates from reputable certificate authorities. When users visit a website, their browser checks the SSL certificate to ensure that it was issued by a trusted authority. If the certificate is not trusted, the browser will display a warning message, which can damage the website’s reputation and deter users from visiting.
In addition, self-signed certificates do not offer the same level of protection as SSL certificates from trusted authorities. They use weaker encryption algorithms, making them vulnerable to hacking attacks. A self-signed certificate might be okay for in-house testing, but when it comes to the public-facing website, don’t compromise on security. Invest in a trusted SSL certificate to ensure that your website is secure and trusted by all.
Myth #3: All SSL Certificates are Created Equal
There’s a myth floating around that all SSL certificates are created equal, but that couldn’t be further from the truth. The fact is SSL certificates come in different types, and each type offers varying levels of validation and security.
At the bottom of the SSL certificate ladder, you have Domain Validated (DV) certificates, which are the least expensive and provide basic encryption for websites. Moving up the ladder, you have Organization Validated (OV) certificates, which provide a higher level of security as they require a more rigorous validation process. And at the top of the ladder, you have Extended Validation (EV) certificates, which are the most expensive and provide the highest level of security, requiring the most rigorous validation process.
It’s important to understand the differences between these types of SSL certificates and choose the one that’s best suited for your website. So don’t fall for the myth that all SSL certificates are the same – take the time to understand your options and choose the best one for your website’s security needs.
Myth #4: HTTPS is a Speed Bump for Your Website
Many website admins think HTTPS is the speed bump on their road to success. But the truth is, HTTPS doesn’t put the brakes on your website’s speed in any noticeable way.
In reality, HTTPS has little to no impact on website speed when set up correctly. Some users may even experience a speed boost when accessing HTTPS-enabled websites through modern browsers. Additionally, using HTTPS provides numerous benefits, such as improved security, privacy, and trustworthiness of your website.
If you’re experiencing significant slowdowns on your HTTPS-enabled website, it’s likely due to other factors, such as improper server configuration or large, uncompressed images. By optimizing these elements, you can ensure that your website is both fast and secure for your users. Don’t let the myth of HTTPS slowing down your website prevent you from taking necessary measures to protect your users’ data and build trust with your audience.
Myth #5: SSL certificates are Too Expensive and Difficult to Obtain
One of the most persistent myths about SSL certificates is that they are too expensive and difficult to obtain. The truth is SSL certificates are now more affordable than ever before, thanks to the availability of various options in the market. For Starters you can check SSLCertShop where you can get Comodo Positive SSL for as less as 5.99$
Obtaining an SSL certificate is also not as difficult as it may seem. In most cases, you can purchase an SSL certificate directly from your web hosting provider or a certificate authority (CA). The process usually involves submitting some basic information and completing a validation process. Once the validation process is complete, you can install the SSL certificate on your website.
Debunk the Myth and Get the SSL-Facts Correct
SSL certificates are essential for website security. They encrypt data, verify the identity of the website owner, and protect sensitive information from being intercepted by hackers. Thus, it is important to understand the myths and misconceptions surrounding SSL certificates to ensure that websites are properly secured. By choosing the appropriate SSL certificate and implementing additional security measures, website owners can ensure that their users’ personal information is protected.











